APIGENIN
Identification
Ingredient |
Apigenin |
Structure:
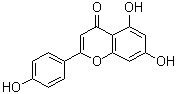 |
Synonyms |
5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one |
Molecular Formula |
C15H10O5 |
Molecular Weight |
270.24 |
CAS no. |
520-36-5 |
EINECS |
208-292-3 |
Description
Pure Apigenin is a yellow crystalline solid. It is sparingly soluble in aqueous buffers,but soluble in organic solvent such as ethanol DMSO and dimethyl formamide.It is suggested to be stored at -20℃,then it should be stable for at least two years.
Scientific support
Apigenin is described as a nonmutagenic bioflavonoid which is presented in leafy plants and vegetables (e.g., parsley, artichoke, basil, celery) and has significant chemopreventive activity against UV-radiation. Current research trials indicate that it may reduce DNA oxidative damage; inhibit the growth of human leukemia cells and induced these cells to differentiate; inhibit cancer cell signal transduction and induce apoptosis; act as an anti-inflammatory; and as an anti-spasmodic or spasmolytic.
As with many flavonoids, apigenin has potential to reduce the risk of cancer since it has anti-tumor activity. Apigenin also could potentially be useful in allergic conditions since it can have anti-inflammatory properties.
Application
According to the US Patent and Trademark Office ( USPTO ), 107 patents involving apigenin in some manner have been obtained in the United States. These patents involve a variety of uses including the preparation of antiviral agents for the treatment of HIV and other infections, particle binders, and pharmaceuticals for treatment of diseases including inflammatory bowel disease and skin conditions ( USPTO, 2000 ).
Apigenin is recognized in traditional or alternative medicine for its pharmacological activity. For this reason, passion flower, which is rich in apigenin, has been used for treating intransigent insomnia, as an anti-spasmodic in Parkinson’s disease and asthma, to reduce nerve pain in neuralgia, and to treat shingles ( Hoffman, 2000a ).
Apigenin is a major constituent of chamomile, which is recognized for its antiphlogistic, antispasmodic, and antibacterial effects. Chamomile tea ( 3-4 cups a day ) has been used for centuries as a folk remedy for relieving indigestion or calming gastritis. Common alternativea are 2-3 grams of the herb in capsule form or 4-6 ml of tincture three times per day. Chamomile preparations are also widely used in skin care products to reduce cutaneous inflammation and other dermatological diseases ( Gruenwald et al., 1998; Healthnotes, 1999; Hoffman, 2000b; Nemecz, 2000 ).
Distribution
Apigenin is found in high amounts in parsley, thyme, and peppermint. Apigenin is also found in a number of herbs, including chamomile herb, lemon balm herb, perilla, vervain herb, and yarrow.
Availability
Commercial Apigenin is obtained by chemical synthesis from Naringin (extracted from immature fruit of Citrus Grandis Osbeck).

Dried immature fruit of Citrus Grandis Osbeck
Warning:
Above information is only knowledge,not an instruction of usage for this product. The owner of this webiste should not be responsible for any damage because of misuse of the product.
|



